Mar 22 , 2024
Medical Tattooing vs. PMU: Key Differences
Medical Tattooing vs. PMU: Key Differences
With the growing popularity of cosmetic and therapeutic tattooing, it's essential to understand that there are differences between medical tattooing and permanent makeup (PMU). While both practices involve tattooing techniques, they serve different purposes and have distinct outcomes. Whether you're a tattoo artist or someone interested in getting a tattoo, it's crucial to have a solid understanding of these specialized fields. In this article, we dive into the core differences between medical tattooing and PMU, providing tattoo artists and enthusiasts with an in-depth understanding of each field. By examining their purposes, techniques, pigment choices, and healing processes, we aim to offer valuable insights into these specialized tattooing practices.
Medical Tattooing: Purpose, Application, Techniques, and Tools

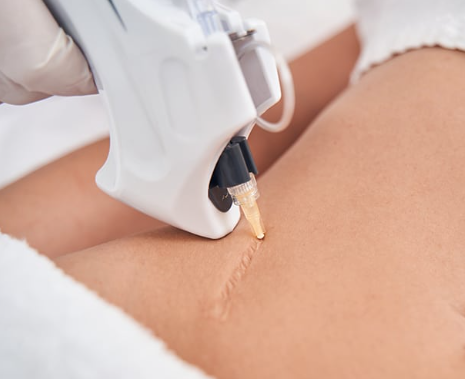
Medical tattooing is a specialized field of tattooing that focuses on concealing or rectifying medical conditions and their effects. It is a therapeutic form of tattooing that aims to heal both physically and emotionally, helping individuals regain confidence and a sense of normalcy after surgery or illness. Some of the most common applications of medical tattooing include areola restoration post-mastectomy, camouflaging scars and vitiligo, and even creating medical alerts (like diabetes) on the skin.

Areola restoration is a procedure that involves the creation of a natural-looking areola and nipple after a mastectomy. This procedure can help women who have undergone a mastectomy regain a sense of femininity and confidence. The tattoo artist uses specialized techniques and tools to create a three-dimensional areola and nipple that closely resemble the original/desired outcome.
2. Scars and Vitiligo:
Medical tattooing can also be used to camouflage scars and vitiligo. This is done by matching the color of the surrounding skin and using specialized techniques to mimic the texture of the skin. The result is a scar that blends in with the surrounding skin, making it less noticeable. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who are self-conscious about their scars or vitiligo.
3. Medical Alerts:
Medical tattooing can also be used to create medical alerts on the skin. For example, individuals with diabetes may choose to have a medical alert tattooed on their arm, alerting medical professionals to their condition in case of an emergency. This can be particularly useful for individuals who are unable to wear medical alert bracelets or necklaces.
Techniques and Tools:

Medical tattooing requires specialized techniques and tools that are designed to mimic the texture and color of the skin or body part being tattooed. The tattoo artist must have a deep understanding of anatomy, color theory, and the psychological impacts of their work. The tools and needles used may vary significantly depending on the specific procedure. For example, areola restoration may require the use of a three-dimensional tattooing technique, while scar camouflage may require the use of a stippling technique.
Pigment Choices:
When it comes to medical tattooing, pigments are chosen based on their ability to accurately mimic natural body colors. This approach requires a thorough understanding of the client's skin tone or the natural coloration of the area being replicated. For example, to create the illusion of an areola after breast reconstruction surgery, the ideal pigment would be one that matches the existing skin tone and texture. Medical tattooing artists have to take into account the healing process, which can be longer, and the retention of pigment, which may differ from healthy skin, requiring touch-ups or color adjustments over time.
Permanent Makeup (PMU): Purpose, Application, Techniques, and Tools

Permanent Makeup (PMU) is a cosmetic form of tattooing that enhances facial features such as eyebrows, eyeliner, and lips. It serves to simplify daily beauty routines, correct asymmetries, and restore features that have faded due to aging or medical conditions like alopecia. PMU focuses on beauty enhancement and the convenience of having long-lasting makeup.
1. Eyebrows:
Eyebrow tattooing, also called Microblading is a popular form of PMU that involves the application of pigment to the eyebrows to enhance their shape and color. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who have thin or sparse eyebrows due to aging or medical conditions like alopecia. The tattoo artist uses specialized techniques and tools to create natural-looking eyebrows that closely resemble real hair.
2. Eyeliner:
Eyeliner tattooing is another popular form of PMU that involves the application of pigment to the eyelids to enhance the appearance of the eyes. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who have difficulty applying eyeliner due to vision problems or shaky hands. The tattoo artist uses specialized techniques and tools to create a natural-looking eyeliner that enhances the eyes.
2. Lip Blushing:

Lip tattooing/blushing is a procedure that involves the application of pigment to the lips to enhance their color and shape. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who have lost color in their lips due to aging or medical conditions or other reasons. The tattoo artist uses specialized techniques and tools to create natural-looking lips that closely resemble real lips.
Techniques and Tools:
PMU involves techniques that replicate the look of cosmetics, requiring precision and artistry to create natural-looking enhancements. The tools used in PMU are often finer and designed for delicate facial work, allowing for the meticulous application of pigment. For example, eyebrow tattooing may require the use of a microblading technique, while lip tattooing may require the use of a lip blush technique.
Pigment Choices:

PMU pigments are selected to emulate conventional makeup colors, with a wide range of shades available to enhance natural features or create the desired cosmetic effect. The application process is less direct and allows for more creativity. For example, a client may want a bold eyeliner or a natural-looking lip tint, and the artist can choose from a range of colors to achieve that look. The pigments used in PMU generally have a more predictable healing process however, factors such as skin type, lifestyle, and exposure to the sun can affect the longevity of PMU.
Healing and Longevity for PMU AND MEDICAL TATTOOING
The healing process and longevity of the results also vary between medical tattooing and PMU.
Medical Tattooing:
Medical tattooing often involves working with scar tissue or sensitive areas recovering from surgery. The prepping and healing process can be longer and more complex. The retention of pigment may differ from healthy skin, requiring touch-ups or color adjustments over time. Scar tissue, for example, may not hold pigment as well as healthy skin. Therefore, medical tattooing may require several sessions to achieve the desired result. Moreover, medical tattooing is often used to correct or camouflage skin irregularities caused by medical conditions or surgery. This means that the tattoo artist must have a thorough understanding of skin anatomy and physiology to achieve the desired result.
Permanent Makeup:
PMU, on the other hand, generally heals more predictably, with results lasting anywhere from one to three years before requiring maintenance. The process involves depositing pigment into the upper layers of the skin, similar to traditional tattooing. However, unlike traditional tattooing, PMU uses a more delicate and precise technique to achieve a more natural and subtle look. The results can be adjusted and refined with touch-ups and color adjustments over time, depending on the client's preferences and lifestyle.
Table: Medical Tattooing vs. PMU at a Glance
|
Feature |
Medical Tattooing |
PMU |
|
Purpose |
Primarily therapeutic, aiming to address and camouflage medical or surgical conditions, and restore natural appearances. |
Cosmetic enhancement, focusing on beauty and the simplification of daily makeup routines. |
|
Applications |
Areola restoration, scar camouflage, vitiligo blending, medical alerts. |
Eyebrows, eyeliner, lip color, beauty marks. |
|
Techniques |
Techniques tailored to mimic the natural appearance of skin, scars, or anatomical features, requiring detailed knowledge of anatomy and skin coloration. |
Techniques designed to replicate the appearance of makeup, emphasizing aesthetic beauty. |
|
Tools and Needles |
Specialized needles and tools adapted for specific medical tattooing tasks, often varying widely to suit different skin textures and conditions. |
Finer, precision tools designed for delicate facial work, allowing for subtle enhancements. |
|
Pigment Choices |
Custom-mixed pigments to closely match the client's skin tone or the natural coloration of the body part being tattooed. |
A wide palette of cosmetic shades designed to mimic conventional makeup colors. |
|
Healing Process |
May involve healing on scar tissue or sensitive areas, potentially leading to longer healing times and variable pigment retention. |
Typically involves a straightforward healing process, with results lasting 1-3 years. |
|
Longevity and Maintenance |
Results may vary depending on the area treated and the type of skin condition, with potential need for touch-ups to maintain appearance. |
Results generally last for 1-3 years, after which maintenance sessions are recommended to refresh the appearance. |
|
Client Impact |
Aimed at psychological and physical rehabilitation, helping individuals feel whole again after trauma or surgery. |
Aimed at enhancing self-esteem and reducing the time and effort spent on daily beauty routines. |
Distinguishing Medical Tattooing and PMU
In conclusion, medical tattooing and PMU are two distinct fields that utilize tattooing techniques to achieve different goals. While medical tattooing helps individuals recover from medical conditions, PMU is focused on enhancing beauty. It is essential for tattoo artists and enthusiasts to understand these differences and cater to the diverse needs of clients. The art of tattooing has the power to transform lives, and it is crucial to remember its profound impact on individuals seeking solace, beauty, and expression through ink. Specialized training and education can help in providing the highest standards of care and craftsmanship. As we continue to explore and push the boundaries of tattooing, let us remember its power to heal and enhance lives.